TrustStore and KeyStore in Kafka
We need to have a secure deployment and encrypted communication on each of these four types of arrows.
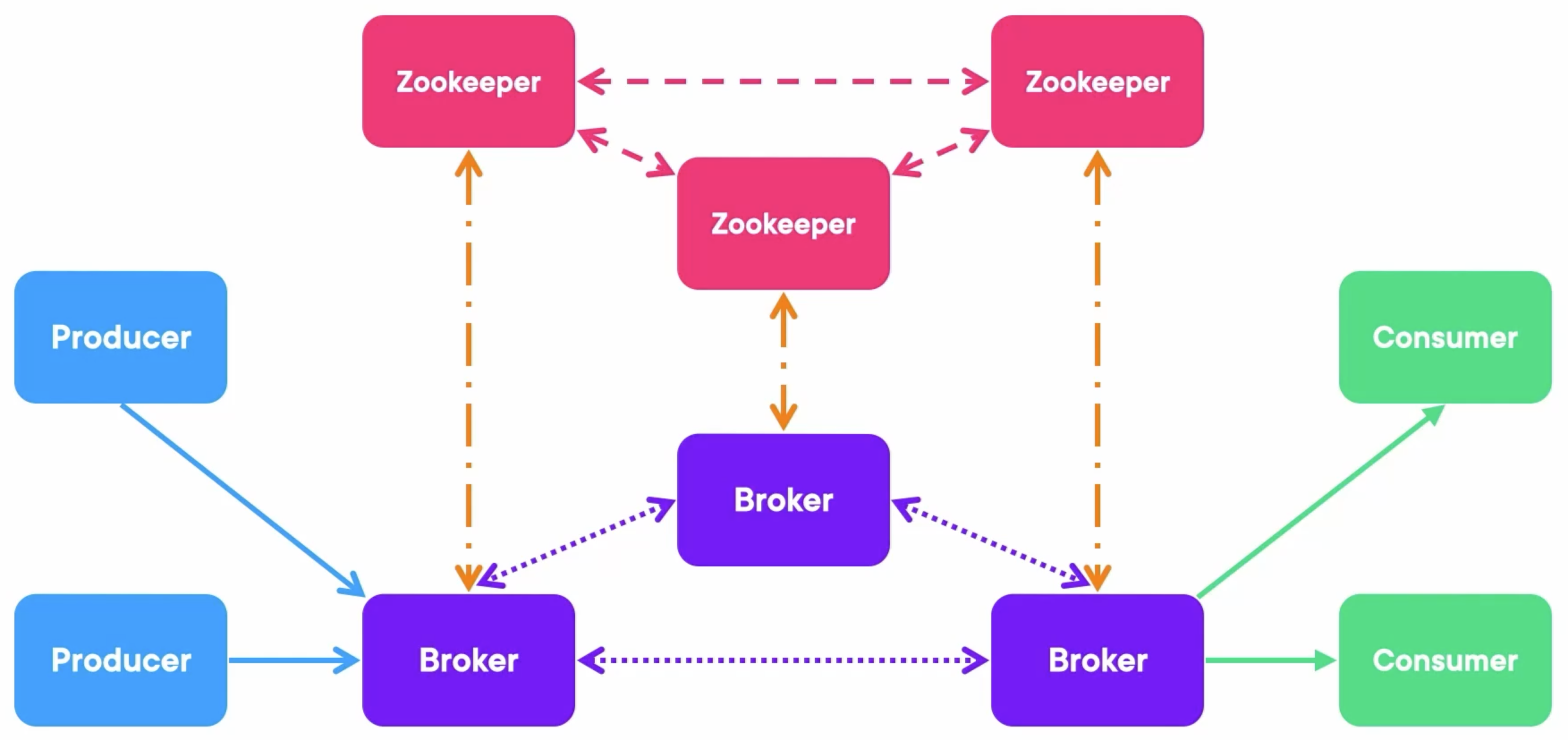
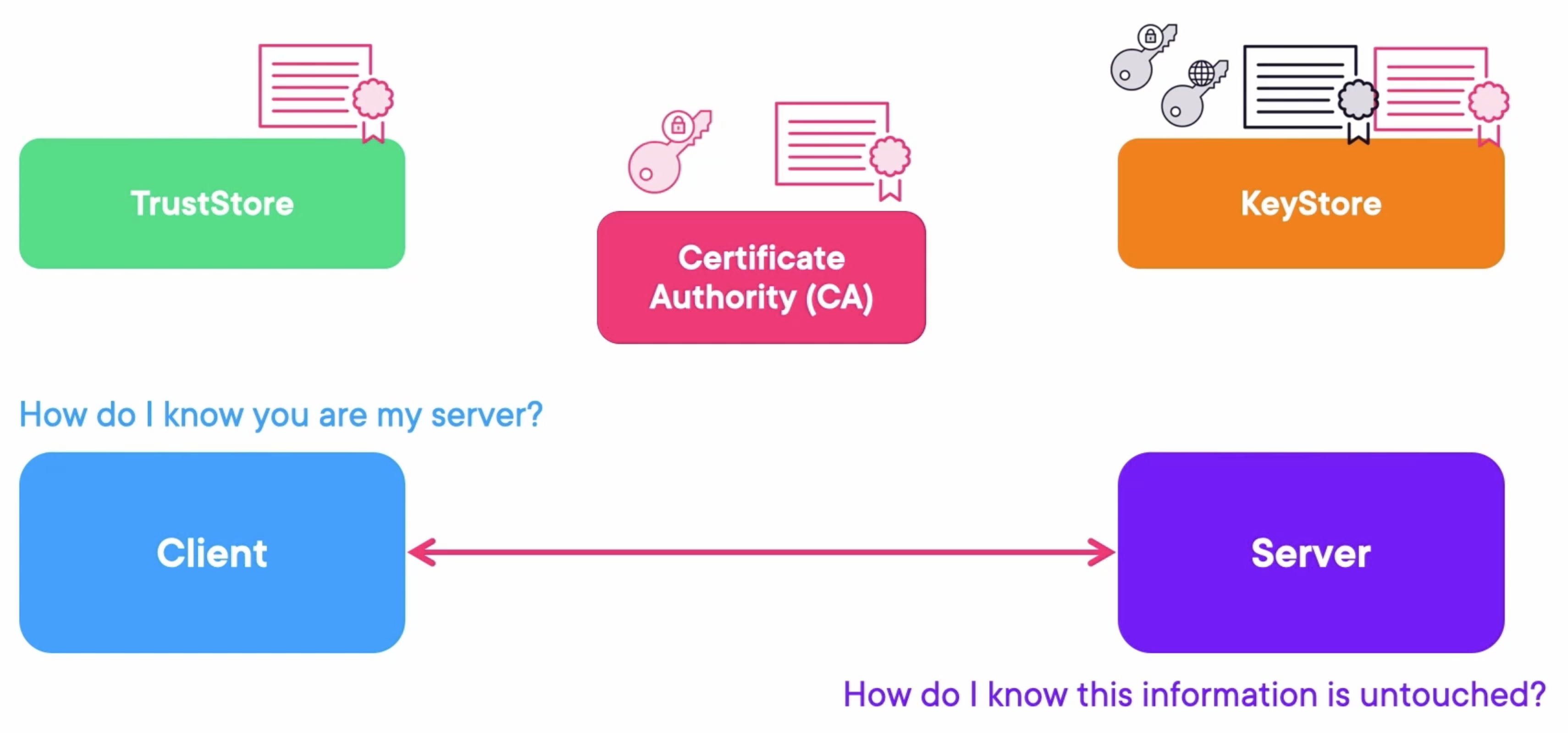
Nowadays, the TLS is mostly used to secure a connection via a CA (Certificate Authority):
- CA (Certificate Authority): The CA can sign other entities certificates.
- Client: The client put certificates in the Trust Store and doesn’t hold keys.
- Server: The server puts certificates, public keys, and private keys in the Key Store.
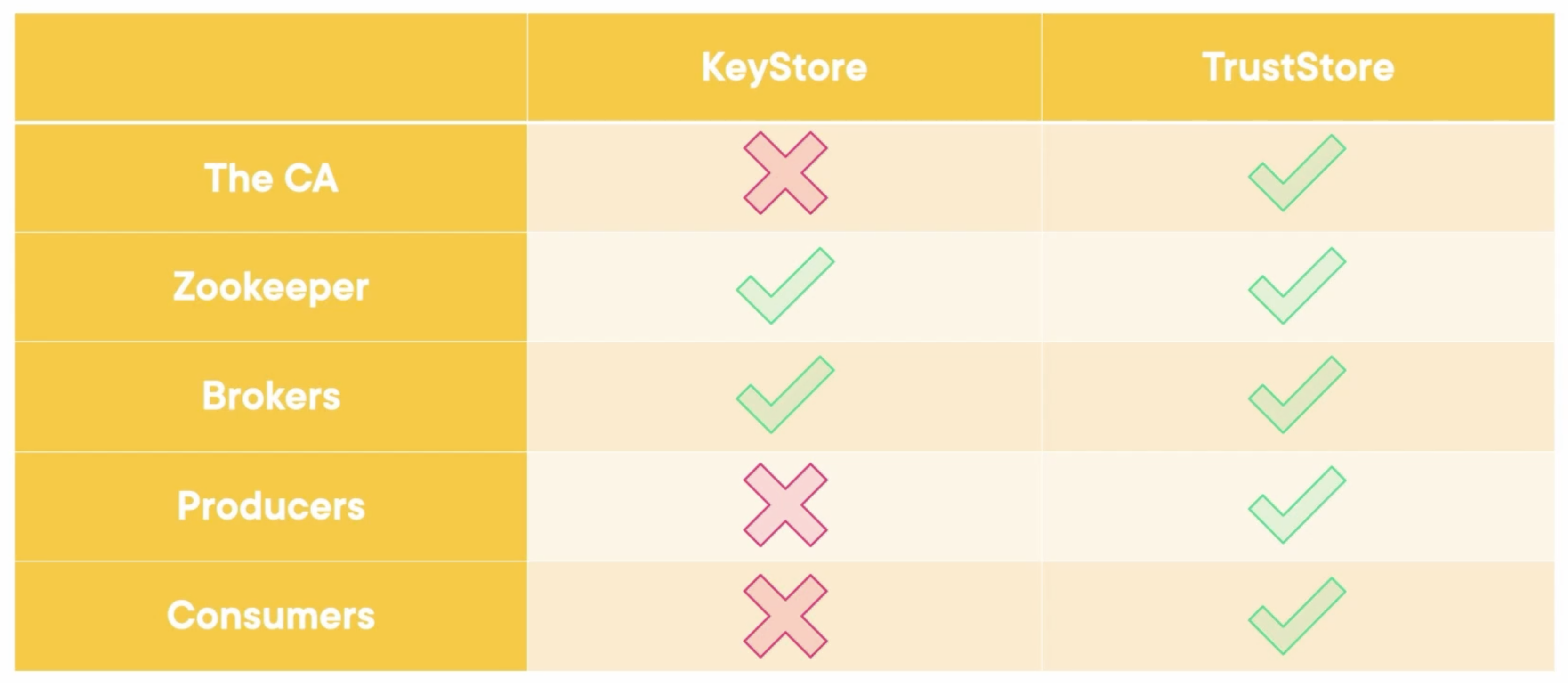
Let’s analyze these five entities in Kafka: the CA, Zookeeper, Brokers, Producers, and Consumers. Who needs a key store, and who needs a trust store, or both?
- The CA: CA is the source of trust, it doesn’t need a keystore to verify against someone and just needs a trust store.
- Zookeepers: They are clients between themselves, so they need a trust store. But they are servers to the brokers, so they also need a key store with a CA certificate and both private and public keys for the brokers. Therefore, they need both.
- Brokers: They are similar to the zookeepers. They are clients between themselves and servers to producers and consumers. Therefore, they need both.
- Producers: They are just clients, so they just need a trust store.
- Consumers: They are just clients, so they just need a trust store.
Demo: Creating the KeyStores and TrustStores
Run Docker Containers
Create a docker-compose file, including three zookeepers, three Kafka brokers, a Rest Proxy, and a Schema Registry.
---
version: '3'
services:
zookeeper-1:
image: confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:7.4.1
hostname: zookeeper-1
container_name: zookeeper-1
volumes:
- ./zookeeper-1_data:/var/lib/zookeeper/data
- ./zookeeper-1_log:/var/lib/zookeeper/log
environment:
ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181
ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000
ZOO_MY_ID: 1
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
zookeeper-2:
image: confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:7.4.1
hostname: zookeeper-2
container_name: zookeeper-2
volumes:
- ./zookeeper-2_data:/var/lib/zookeeper/data
- ./zookeeper-2_log:/var/lib/zookeeper/log
environment:
ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181
ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000
ZOO_MY_ID: 2
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
zookeeper-3:
image: confluentinc/cp-zookeeper:7.4.1
hostname: zookeeper-3
container_name: zookeeper-3
volumes:
- ./zookeeper-3_data:/var/lib/zookeeper/data
- ./zookeeper-3_log:/var/lib/zookeeper/log
environment:
ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181
ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000
ZOO_MY_ID: 3
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=zookeeper-1:2888:3888;2181 server.2=zookeeper-2:2888:3888;2181 server.3=zookeeper-3:2888:3888;2181
broker-1:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.4.1
hostname: broker-1
container_name: broker-1
volumes:
- ./broker-1-data:/var/lib/kafka/data
depends_on:
- zookeeper-1
- zookeeper-2
- zookeeper-3
ports:
- 9092:9092
- 29092:29092
environment:
KAFKA_BROKER_ID: 1
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper-1:2181
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: HOST://localhost:9092,INTERNAL://broker-1:29092
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: HOST:PLAINTEXT,INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: INTERNAL
KAFKA_SNAPSHOT_TRUST_EMPTY: true
broker-2:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.4.1
hostname: broker-2
container_name: broker-2
volumes:
- ./broker-2-data:/var/lib/kafka/data
depends_on:
- zookeeper-1
- zookeeper-2
- zookeeper-3
- broker-1
ports:
- 9093:9093
- 29093:29093
environment:
KAFKA_BROKER_ID: 2
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper-1:2181
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: HOST://localhost:9093,INTERNAL://broker-2:29093
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: HOST:PLAINTEXT,INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: INTERNAL
KAFKA_SNAPSHOT_TRUST_EMPTY: true
broker-3:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.4.1
hostname: broker-3
container_name: broker-3
volumes:
- ./broker-3-data:/var/lib/kafka/data
depends_on:
- zookeeper-1
- zookeeper-2
- zookeeper-3
- broker-1
- broker-2
ports:
- 9094:9094
- 29094:29094
environment:
KAFKA_BROKER_ID: 3
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper-1:2181
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: HOST://localhost:9094,INTERNAL://broker-3:29094
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: HOST:PLAINTEXT,INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: INTERNAL
KAFKA_SNAPSHOT_TRUST_EMPTY: true
rest-proxy:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka-rest:7.4.1
ports:
- "8082:8082"
depends_on:
- zookeeper-1
- zookeeper-2
- zookeeper-3
- broker-1
- broker-2
- broker-3
hostname: rest-proxy
container_name: rest-proxy
environment:
KAFKA_REST_HOST_NAME: rest-proxy
KAFKA_REST_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: 'broker-1:29092,broker-2:29093,broker-3:29094'
KAFKA_REST_LISTENERS: "http://0.0.0.0:8082"
schema-registry:
image: confluentinc/cp-schema-registry:7.4.1
hostname: schema-registry
container_name: schema-registry
depends_on:
- rest-proxy
ports:
- "8081:8081"
environment:
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOST_NAME: schema-registry
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: 'broker-1:29092,broker-2:29093,broker-3:29094'
Run composed containers:
docker compose up -d
Create a Topic
Create a myorders topic that has four partitions.
kafka-topics.sh --create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --partitions 4 --topic myorders
Generate the Certificate Authority
Create a shell script file generate-called.sh like the following:
VALIDITY_DAYS=36500
CA_KEY_FILE="ca-key"
CA_CERT_FILE="ca-cert"
openssl req -new -x509 -keyout $CA_KEY_FILE -out $CA_CERT_FILE -days $VALIDITY_DAYS
#### Example Values ####
# Passphrase: password
# Country Name: US
# State or Province: UT
# City: Utah
# Organization Name: zjxjwxk
# Organizational Unit Name: zjxjwxk
# Common Name: zjxjwxk.github.io
# Email: zjxjwxk@gmail.com
Run the script and input all information it needs:
❯ ./generate-ca.sh
......+......+..+......+.........+.+......+...............+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*.+....+.........+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*..+.........+......++++++
....+.....+...+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*...+...+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*.........+...+....+............+........+.....................+......+.+...+.....+.......+...+.................+.........+...............+.+...+..+.........+...+.+...................................+.+.....+....+..++++++
Enter PEM pass phrase:
Verifying - Enter PEM pass phrase:
-----
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:UT
Locality Name (eg, city) []:Utah
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:zjxjwxk
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:zjxjwxk
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:zjxjwxk.github.io
Email Address []:zjxjwxk@gmail.com
Generate the KeyStores
Create a shell script file generate-keystore.sh like the following:
COMMON_NAME=$1
ORGANIZATIONAL_UNIT="zjxjwxk"
ORGANIZATION="zjxjwxk"
CITY="Utah"
STATE="UT"
COUNTRY="US"
CA_ALIAS="ca-root"
CA_CERT_FILE="ca-cert"
VALIDITY_DAYS=36500
# Generate Keystore with Private Key
keytool -keystore keystore/$COMMON_NAME.keystore.jks -alias $COMMON_NAME -validity $VALIDITY_DAYS -genkey -keyalg RSA -dname "CN=$COMMON_NAME, OU=$ORGANIZATIONAL_UNIT, O=$ORGANIZATION, L=$CITY, ST=$STATE, C=$COUNTRY"
# Generate Certificate Signing Request (CSR) using the newly created KeyStore
keytool -keystore keystore/$COMMON_NAME.keystore.jks -alias $COMMON_NAME -certreq -file $COMMON_NAME.csr
# Sign the CSR using the custom CA
openssl x509 -req -CA ca-cert -CAkey ca-key -in $COMMON_NAME.csr -out $COMMON_NAME.signed -days $VALIDITY_DAYS -CAcreateserial
# Import ROOT CA certificate into Keystore
keytool -keystore keystore/$COMMON_NAME.keystore.jks -alias $CA_ALIAS -importcert -file $CA_CERT_FILE
# Import newly signed certificate into Keystore
keytool -keystore keystore/$COMMON_NAME.keystore.jks -alias $COMMON_NAME -importcert -file $COMMON_NAME.signed
# Clean-up
rm $COMMON_NAME.csr
rm $COMMON_NAME.signed
rm ca-cert.srl
Create the keystore folder in the same path and then run the script with a parameter, which will be the name using the key store (run this script 6 times for three brokers and three zookeepers), and then input the passphrase when needed:
❯ ./generate-keystore.sh broker-1
输入密钥库口令:
再次输入新口令:
输入 <broker-1> 的密钥口令
(如果和密钥库口令相同, 按回车):
Warning:
JKS 密钥库使用专用格式。建议使用 "keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -destkeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -deststoretype pkcs12" 迁移到行业标准格式 PKCS12。
输入密钥库口令:
Warning:
JKS 密钥库使用专用格式。建议使用 "keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -destkeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -deststoretype pkcs12" 迁移到行业标准格式 PKCS12。
Certificate request self-signature ok
subject=C=US, ST=UT, L=Utah, O=zjxjwxk, OU=zjxjwxk, CN=broker-1
Enter pass phrase for ca-key:
输入密钥库口令:
所有者: EMAILADDRESS=zjxjwxk@gmail.com, CN=zjxjwxk.github.io, OU=zjxjwxk, O=zjxjwxk, L=Utah, ST=UT, C=US
发布者: EMAILADDRESS=zjxjwxk@gmail.com, CN=zjxjwxk.github.io, OU=zjxjwxk, O=zjxjwxk, L=Utah, ST=UT, C=US
序列号: 7f8120f61b9782eadb2fd5097a6e58e116ba5351
有效期为 Sun Mar 16 15:13:13 CST 2025 至 Tue Feb 20 15:13:13 CST 2125
证书指纹:
MD5: AE:1E:A0:89:D6:FC:FF:6C:73:83:A8:8E:72:EC:5C:14
SHA1: 27:BD:36:3A:64:92:08:BF:C5:93:EA:50:EC:B6:39:53:08:30:C9:96
SHA256: 7A:1A:E0:6D:91:C1:5E:FE:D1:6A:81:27:13:3E:08:5C:6A:D7:AF:A0:14:B4:C1:43:AA:65:85:AF:DC:B8:04:ED
签名算法名称: SHA256withRSA
主体公共密钥算法: 2048 位 RSA 密钥
版本: 3
扩展:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.35 Criticality=false
AuthorityKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: 85 57 ED 32 DF F0 D2 E5 4B E9 DF 4E 77 5E 3B CA .W.2....K..Nw^;.
0010: 03 91 17 70 ...p
]
]
#2: ObjectId: 2.5.29.19 Criticality=true
BasicConstraints:[
CA:true
PathLen:2147483647
]
#3: ObjectId: 2.5.29.14 Criticality=false
SubjectKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: 85 57 ED 32 DF F0 D2 E5 4B E9 DF 4E 77 5E 3B CA .W.2....K..Nw^;.
0010: 03 91 17 70 ...p
]
]
是否信任此证书? [否]: y
证书已添加到密钥库中
Warning:
JKS 密钥库使用专用格式。建议使用 "keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -destkeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -deststoretype pkcs12" 迁移到行业标准格式 PKCS12。
输入密钥库口令:
证书回复已安装在密钥库中
Warning:
JKS 密钥库使用专用格式。建议使用 "keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -destkeystore keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks -deststoretype pkcs12" 迁移到行业标准格式 PKCS12。
Create the Truststores
Create a shell script file generate-truststore.sh like the following:
INSTANCE=$1
CA_ALIAS="ca-root"
CA_CERT_FILE="ca-cert"
#### Generate Truststore and import ROOT CA certificate ####
keytool -keystore truststore/$INSTANCE.truststore.jks -import -alias $CA_ALIAS -file $CA_CERT_FILE
Create the truststroe folder in the same path and then run the script with a parameter, which will be the name using the trust store (run this script 6 times for three brokers and three zookeepers), and then input the passphrase when needed:
❯ ./generate-truststore.sh broker-1
输入密钥库口令:
再次输入新口令:
所有者: EMAILADDRESS=zjxjwxk@gmail.com, CN=zjxjwxk.github.io, OU=zjxjwxk, O=zjxjwxk, L=Utah, ST=UT, C=US
发布者: EMAILADDRESS=zjxjwxk@gmail.com, CN=zjxjwxk.github.io, OU=zjxjwxk, O=zjxjwxk, L=Utah, ST=UT, C=US
序列号: 7f8120f61b9782eadb2fd5097a6e58e116ba5351
有效期为 Sun Mar 16 15:13:13 CST 2025 至 Tue Feb 20 15:13:13 CST 2125
证书指纹:
MD5: AE:1E:A0:89:D6:FC:FF:6C:73:83:A8:8E:72:EC:5C:14
SHA1: 27:BD:36:3A:64:92:08:BF:C5:93:EA:50:EC:B6:39:53:08:30:C9:96
SHA256: 7A:1A:E0:6D:91:C1:5E:FE:D1:6A:81:27:13:3E:08:5C:6A:D7:AF:A0:14:B4:C1:43:AA:65:85:AF:DC:B8:04:ED
签名算法名称: SHA256withRSA
主体公共密钥算法: 2048 位 RSA 密钥
版本: 3
扩展:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.35 Criticality=false
AuthorityKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: 85 57 ED 32 DF F0 D2 E5 4B E9 DF 4E 77 5E 3B CA .W.2....K..Nw^;.
0010: 03 91 17 70 ...p
]
]
#2: ObjectId: 2.5.29.19 Criticality=true
BasicConstraints:[
CA:true
PathLen:2147483647
]
#3: ObjectId: 2.5.29.14 Criticality=false
SubjectKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: 85 57 ED 32 DF F0 D2 E5 4B E9 DF 4E 77 5E 3B CA .W.2....K..Nw^;.
0010: 03 91 17 70 ...p
]
]
是否信任此证书? [否]: y
证书已添加到密钥库中
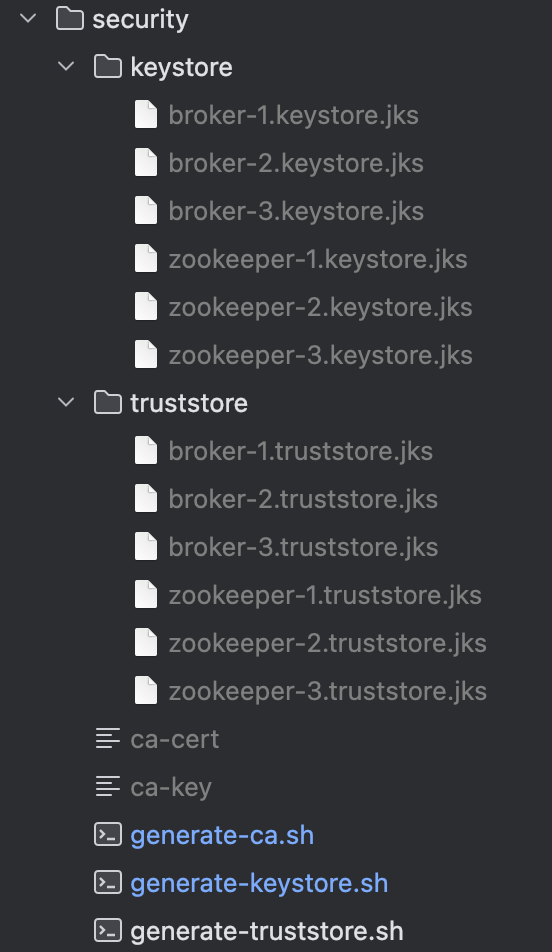
Finally, the generated key stores and trust stores should look like this:
Encrypt Zookeeper
Encrypting Zookeeper can be done in two ways: Online Fashion and Offline Fashion.
The configuration we need to add to each Zookeeper in the docker-compose file:
zookeeper-1:
...
volumes:
...
- ./security/keystore/zookeeper-1.keystore.jks:/security/zookeeper-1.keystore.jks
- ./security/truststore/zookeeper-1.truststore.jks:/security/zookeeper-1.truststore.jks
environment:
...
ZOO_CFG_EXTRA: "sslQuorum=true
portUnification=false
serverCnxnFactory=org.apache.zookeeper.server.NettyServerCnxnFactory
ssl.quorum.hostnameVerification=false
ssl.quorum.keyStore.location=/security/zookeeper-1.keystore.jks
ssl.quorum.keyStore.password=password
ssl.quorum.trustStore.location=/security/zookeeper-1.truststore.jks
ssl.quorum.trustStore.password=password
secureClientPort=2281
ssl.hostnameVerification=false
ssl.keyStore.location=/security/zookeeper-1.keystore.jks
ssl.keyStore.password=password
ssl.trustStore.location=/security/zookeeper-1.truststore.jks
ssl.trustStore.password=password"
The configuration we need to add to each broker in the docker-compose file:
broker-1:
...
volumes:
...
- ./security/keystore/broker-1.keystore.jks:/kafka/security/broker-1.keystore.jks
- ./security/truststore/broker-1.truststore.jks:/kafka/security/broker-1.truststore.jks
environment:
...
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_SSL_CLIENT_ENABLE: "true"
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_CNXN_SOCKET: org.apache.zookeeper.ClientCnxnSocketNetty
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_SSL_KEYSTORE_LOCATION: /kafka/security/broker-1.keystore.jks
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_SSL_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD: password
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION: /kafka/security/broker-1.truststore.jks
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: password
Encrypt Producers and Consumers
Configuration
Four supported protocols are PLAINTEXT, SSL, SASL_PLAINTEXT, and SASL_SSL. (SASL involves authentication).
Declaring a listener is quite simple as well, in the environment we need to set:
broker-1:
...
environment:
...
KAFKA_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://broker-1:9091
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://broker-1:9091
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT
If we want to use SSL, we need to change those to:
broker-1:
...
environment:
...
KAFKA_LISTENERS: SSL://broker-1:9192
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: SSL://broker-1:9192
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: SSL:SSL
KAFKA_SECURITY_INTER_BROKER_PROTOCOL: SSL
KAFKA_SSL_CLIENT_AUTH: none
Set the TrustStores and KeyStores:
broker-1:
...
environment:
...
KAFKA_SSL_KEYSTORE_LOCATION: /kafka/security/broker-1.keystore.jks
KAFKA_SSL_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD: password
KAFKA_SSL_KEY_PASSWORD: passowrd
KAFKA_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION: /kafka/security/broker-1.truststore.jks
KAFKA_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: password
Consumer and Producer using SSL in Java
The difference between a consumer using SSL and a consumer using plaintext is that:
Change the ports of each broker configured to the
ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIGto the ports using SSL.props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "broker-1:9191,broker-2:9192,broker-3:9193");
Set the
CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIGto SSL.props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SSL");
Set the trust store key and the password.
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, "/Users/zjxjwxk/Documents/Project/getting-started-kafka/module8/demo3/security/truststore/consumer.truststore.jks"); // Replace with the absolute path on your machine props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, "password");
The consumer using SSL should be like:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.CommonClientConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import org.apache.kafka.common.config.SslConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class BasicSSLConsumer {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BasicSSLConsumer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "broker-1:9191,broker-2:9192,broker-3:9193");
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName());
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName());
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "basic.consumer");
props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SSL");
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, "/Users/zjxjwxk/Documents/Project/getting-started-kafka/module8/demo3/security/truststore/consumer.truststore.jks"); // Replace with the absolute path on your machine
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, "password");
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props);
Thread haltedHook = new Thread(consumer::close);
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(haltedHook);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("basic-topic"));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
records.forEach(record -> log.info("Consumed message: " + record.key() + ":" + record.value()));
}
}
}
The producer is similar:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.CommonClientConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.*;
import org.apache.kafka.common.config.SslConfigs;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class BasicSSLProducer {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BasicSSLProducer.class);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "broker-1:9191,broker-2:9192,broker-3:9193");
props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());
props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringSerializer.class.getName());
props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SSL");
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, "/Users/zjxjwxk/Documents/Project/getting-started-kafka/module8/demo3/security/truststore/producer.truststore.jks"); // Replace with the absolute path on your machine
props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, "password");
KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
Thread haltedHook = new Thread(producer::close);
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(haltedHook);
long i = 0;
while(true) {
String key = String.valueOf(i);
String value = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
ProducerRecord<String, String> producerRecord =
new ProducerRecord<>("basic-topic", key, value);
producer.send(producerRecord);
log.info("Message sent: " + key + ":" + value);
i++;
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
}
Monitoring Kafka: Scaling
Cluster Level
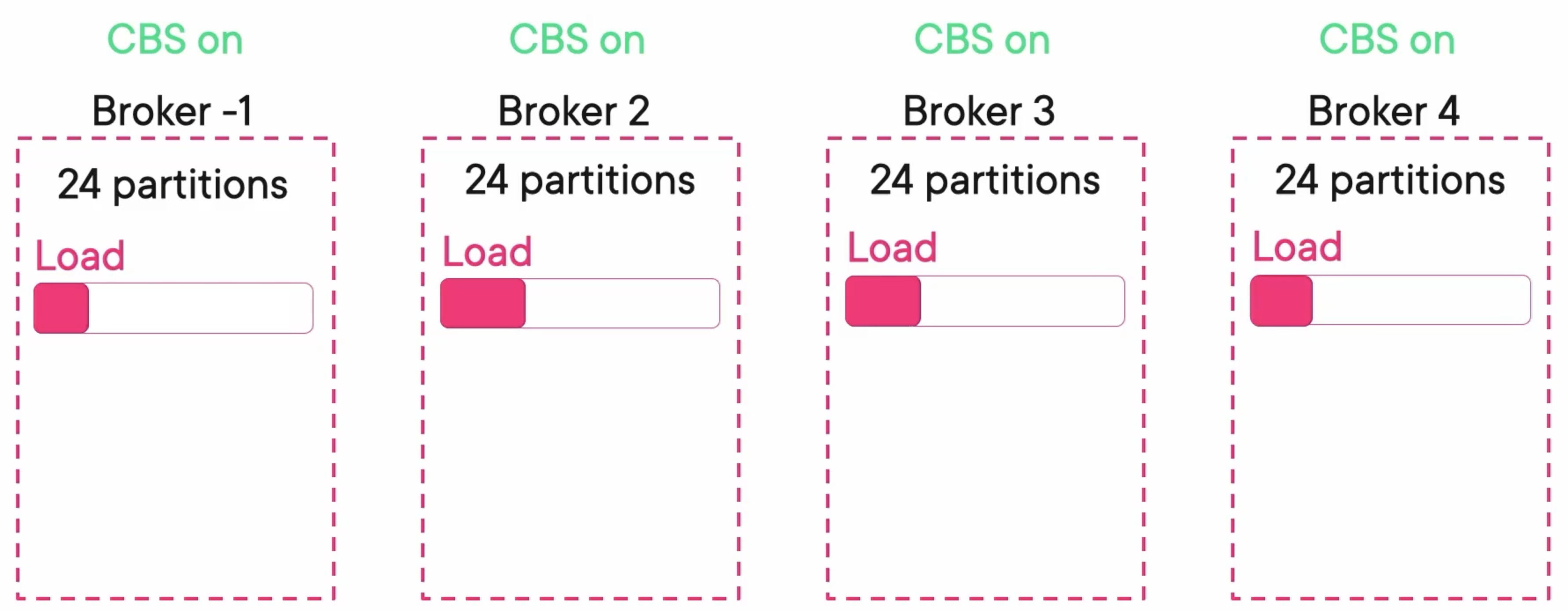
If there are some problems with the cluster level, usually means a high load. Add a broker 4 and turn on the balancer. Then the load will be balanced between brokers.
confluent.balancer.enable=true
Broker Level
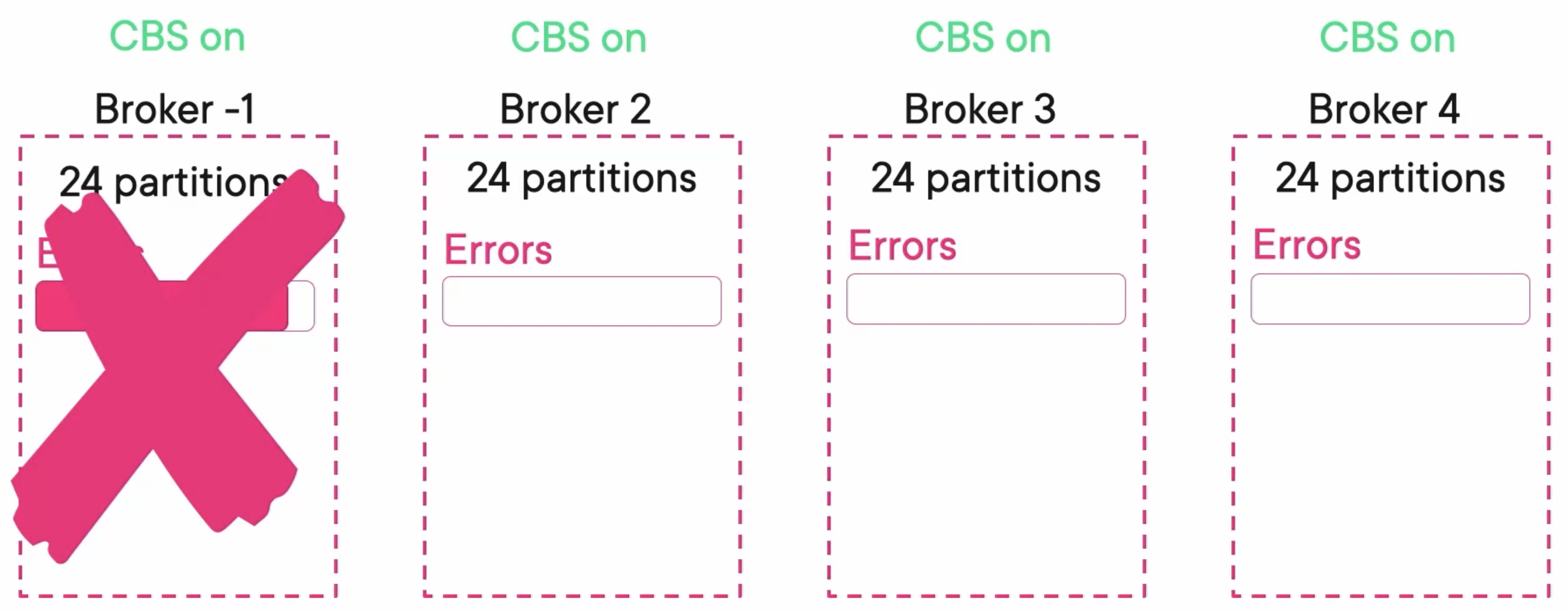
If there are some problems with the broker level. We can just restart the broker.
Topic Level
The only problem that load balancer from confluent doesn’t detect is the topic level. To detect that, the command to run is:
❯ kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group 1
GROUP TOPIC PARTITION CURRENT-OFFSET LOG-END-OFFSET LAG CONSUMER-ID HOST CLIENT-ID
1 myorders 1 0 0 0 console-consumer-8a295fc9-0d1f-4712-9c60-8e5ce13c7155 /172.30.0.1 console-consumer
1 myorders 0 0 0 0 console-consumer-8a295fc9-0d1f-4712-9c60-8e5ce13c7155 /172.30.0.1 console-consumer%
If a topic’s LAG is high, the consumer is not catching up, which means we need more partitions.
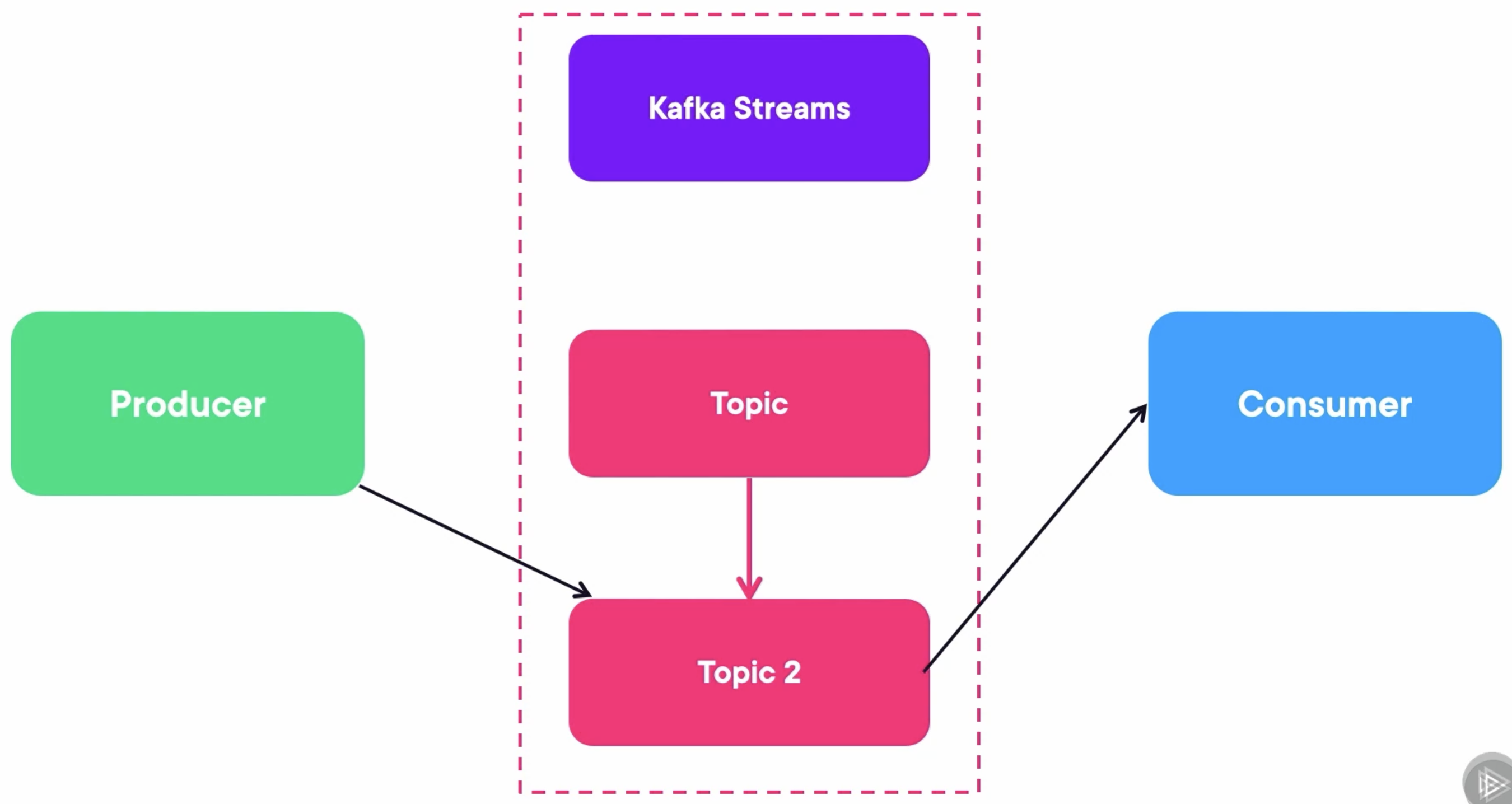
Increasing the number of partitions of a topic is not easy. The best way is:
- Create another topic with more partitions.
- Then create a Kafka Streams application that will read from the original topic and write to the output topic. When that steam application is done, then there is no lag.
- Migrate producers and consumers to the new topic.
Takeaway
- We need to secure all communications channels in Kafka by encrypting them with TLS.
- We created TrustStroes for all entities and KeyStores for Brokers and Zookeepers.
- To scale out Kafka, most of the problems are solved by the Confluent tool, SBC (Self-Balancing Clusters).